Oracle hfm beginner's guide part i
- 1. http://learnhyperion.wordpress.com Oracle Hyperion Financial Management 11.1.1.3 Beginner’s Guide Part I Provided By: BISP Created By: Rupam Majumdar http://bispsolutions.wordpress.com Amit Sharma bisp.consulting@gmail.com BISP Team http://learnhyperion.wordpress.com ©Business Intelligence Solution Providers learnhyperion.wordpress.com aloo_a2@yahoo.com 1
- 2. http://learnhyperion.wordpress.com Problem and Challenges Many finance executives face the daunting task of consolidating their company’s financial and operating results using spreadsheets that are difficult to maintain and audit. Some are encumbered with custom reporting solutions that don’t scale or address global requirements, while others are dependent on general ledger-based approaches that can’t pull data from numerous transactional systems without significant IT support. What is needed is a single version of the truth-one view of financial and operational results integrated from multiple systems - without delays. Why HFM PLAN + Powerful FEATURES + Design Considerations + Reporting Tools = Ø Less confusion Less time Ø Shorter closes and Transforms data into usable information Ø Viable WEB delivery mechanisms Ø Process management for tight control of the review and approval process Ø Data Validation Ø Currency translation to support multiple local currencies. Ø Automatic elimination for intercompany data and transactions. ©Business Intelligence Solution Providers learnhyperion.wordpress.com aloo_a2@yahoo.com 2
- 3. http://learnhyperion.wordpress.com Hyperion Financial Management “Financial Management is a comprehensive, Web-Based application that enables you to manage enterprise financial information quickly and cost effectively. Financial Management delivers global data collection, financial consolidation, reporting and analysis in single highly scalable solutions.” HFM excels at: ©Business Intelligence Solution Providers learnhyperion.wordpress.com aloo_a2@yahoo.com 3
- 4. http://learnhyperion.wordpress.com Complex Organizational Consolidation • Multiple Transactional Currencies • Intercompany Transactions • Minority Interest • Maintaining Historical Representation of Data • Ability to handle Journals • Full Audit Trails – – Data & End User Actions • External Reporting to Stakeholders ©Business Intelligence Solution Providers learnhyperion.wordpress.com aloo_a2@yahoo.com 4
- 5. http://learnhyperion.wordpress.com Product Architecture Financial Management uses a multitier architecture that includes a client tier, an application tier, and a database tier. The client tier contains the user interface. It communicates with the application tier. The primary function of the client tier is to display, enter, and maintain data and to maintain metadata. The application tier contains the application, the report, and Web servers. The Web server enables you to access the Web-based portions of Financial Management. The application server contains the financial intelligence and connections to the relational database and OLAP engine. It also contains Architect for managing metadata. The data tier contains the relational databases for Financial Management metadata and source data. ©Business Intelligence Solution Providers learnhyperion.wordpress.com aloo_a2@yahoo.com 5
- 6. http://learnhyperion.wordpress.com Financial Management Overview Financial Management is a powerful application that enables you to manage enterprise financial information quickly and cost effectively. You follow a typical task flow for a monthly financial cycle. TASK DESCRIPTION Load and add data To add data to your application by loading it from a file and by using data forms. Calculate After enter data, you can run calculation rules to populate calculated accounts. Adjust data After you calculate data, you can adjust the data by using journals that provide an audit trail of your adjustments. Translate and After data for individual business units is entered and consolidate data adjusted, you can translate and consolidate the data. ©Business Intelligence Solution Providers learnhyperion.wordpress.com aloo_a2@yahoo.com 6
- 7. http://learnhyperion.wordpress.com Approve data After data is consolidated, you can submit the data for review and approval. Lock data After you receive the approval for the submitted data, you can lock the data to prevent further modifications. Run and publish You can run reports against the approved data. financial reports With Financial Management we can able to Ø Conduct in-depth analysis of key performance and operational metrics. Ø Reduce consolidation and reporting cycle by days or weeks. Ø Deliver accurate and timely reports to both internal management and external regulatory bodies. Ø Discover sources of profitability and cash flow at the company, product, brand, and customer levels. ©Business Intelligence Solution Providers learnhyperion.wordpress.com aloo_a2@yahoo.com 7
- 8. http://learnhyperion.wordpress.com Financial Management Components Financial Management integrates application creation and management in a centralized administration environment. Ø Single sign-on—Users log on once to Workspace to access Architect, Financial Management, and the reporting tools. Ø Single console for application management and creation—Users create, manage, and deploy applications from Architect. These applications are opened in Financial Management for data retrieval and data output. Ø Centralized repository of key dimensional elements for different products. Ø Centralized console for controlling data flow between applications. ©Business Intelligence Solution Providers learnhyperion.wordpress.com aloo_a2@yahoo.com 8
- 9. http://learnhyperion.wordpress.com Financial Consolidation, Reporting & Analysis Financial Management enables highly efficient collection and consolidation of data from diverse sources. It includes these features: • Process management for tight control of the review and approval process. • Data validation. • Currency translation to support multiple local currencies. • Automatic eliminations for intercompany transactions. Financial Management is designed for large-scale, centralized Web deployment. You can use Financial Management to consolidate data from diverse general ledger systems and locations around the globe. ©Business Intelligence Solution Providers learnhyperion.wordpress.com aloo_a2@yahoo.com 9
- 10. http://learnhyperion.wordpress.com SEC – The U.S. Reporting Standard Principles-based Ø Does not replace framework requirements Ø Focus on areas of highest risk of material misstatement to financial statements Ø Management flexibility to tailor evaluation process to specific facts and circumstances Ø Provides guidance on supporting the assessment Ø Provides framework for evaluating deficiencies ©Business Intelligence Solution Providers learnhyperion.wordpress.com aloo_a2@yahoo.com 10
- 11. http://learnhyperion.wordpress.com THE SEC WORKFLOW ©Business Intelligence Solution Providers learnhyperion.wordpress.com aloo_a2@yahoo.com 11
- 12. http://learnhyperion.wordpress.com 10K- 10Q The 10-K explains the company's business activities for the most recent twelve- month operating period. The 10-K, which is required to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) within 90 days of the company's fiscal year end, typically contains more detail than an annual report, such as more thorough operating and financial statistics, information on legal proceedings, and management compensation. Form 100Qs a quarterly version of the 10-K; however, it is less detailed and generally unaudited. The SEC requires publicly traded companies to file form 10- Q within 45 days of the end of each quarter, except the final quarter, in which the 10-K is filed. ©Business Intelligence Solution Providers learnhyperion.wordpress.com aloo_a2@yahoo.com 12
- 13. http://learnhyperion.wordpress.com THE REPORT GENERATED Financial Management Dimensions Dimensions describe an organization’s data and usually contain groups of related members. Examples of dimensions are Account, Entity, and Period. Financial Management supplies eight system-defined dimensions and enables you to populate up to four custom dimensions that you can apply to accounts. Dimension members are arranged in hierarchies. Upper-level members are called parent members, and a member immediately below a parent member is referred to as the child of a parent member. All members below a parent are referred to as descendants. The bottom- level hierarchy members are called base-level-members. ©Business Intelligence Solution Providers learnhyperion.wordpress.com aloo_a2@yahoo.com 13
- 14. http://learnhyperion.wordpress.com THE POWER OF GOOD DIMENSIONALITY ©Business Intelligence Solution Providers learnhyperion.wordpress.com aloo_a2@yahoo.com 14
- 15. http://learnhyperion.wordpress.com ©Business Intelligence Solution Providers learnhyperion.wordpress.com aloo_a2@yahoo.com 15
- 16. http://learnhyperion.wordpress.com Scenario Dimension The Scenario dimension represents a set of data, such as Budget, Actual, or Forecast. For example, the Actual scenario can contain data from a general ledger, reflecting past and current business operations. The Budget scenario can contain data that reflects the targeted business operations. The Forecast scenario typically contains data that corresponds to predictions for upcoming periods. A Legal scenario can contain data calculated according to legal GAAP format and rules. You can define any number of scenarios for an application and define attributes for Scenario dimension members, such as the default frequency, the default view, and zero data settings. Year Dimension The Year dimension represents the fiscal or calendar year for data. An application can contain data for more than one year. You specify a year range when you create the application and select a year from the Year dimension to process data. ©Business Intelligence Solution Providers learnhyperion.wordpress.com aloo_a2@yahoo.com 16
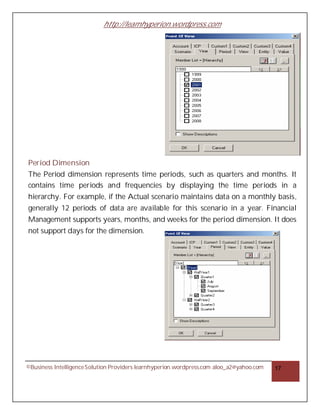
- 17. http://learnhyperion.wordpress.com Period Dimension The Period dimension represents time periods, such as quarters and months. It contains time periods and frequencies by displaying the time periods in a hierarchy. For example, if the Actual scenario maintains data on a monthly basis, generally 12 periods of data are available for this scenario in a year. Financial Management supports years, months, and weeks for the period dimension. It does not support days for the dimension. ©Business Intelligence Solution Providers learnhyperion.wordpress.com aloo_a2@yahoo.com 17
- 18. http://learnhyperion.wordpress.com Entity Dimension The Entity dimension represents the organizational structure of the company, such as the management and legal reporting structures. Entities can represent divisions, subsidiaries, plants, regions, countries, legal entities, business units, departments, or any organizational unit. You can define any number of entities. The Entity dimension is the consolidation dimension of the system. Hierarchies in the Entity dimension reflect various consolidated views of the data. Various hierarchies can correspond to geographic consolidation, legal consolidation, or consolidation by activity. All relationships among individual member components that exist in an organization are stored and maintained in this dimension. Entities in an organization are dependent, base, or parent entities. Dependent entities are owned by other entities in the organization. Base entities are at the bottom of the organization structure and do not own other entities. Parent entities contain one or more dependents that report directly to them. You define attributes for Entity dimension members, such as the default currency and security class, and to specify whether the entity allows adjustments and stores intercompany detail. Financial Management Dimensions. ©Business Intelligence Solution Providers learnhyperion.wordpress.com aloo_a2@yahoo.com 18
- 19. http://learnhyperion.wordpress.com Value Dimension The Value dimension represents the different types of values stored in your application, and can include the input currency, parent currency, adjustments, and consolidation detail such as proportion, elimination, and contribution detail. For example, the Entity Currency member stores the value for an entity in its local currency. The Parent Currency member stores the value for an entity translated the currency of its parent entity. Account Dimension The Account dimension represents a hierarchy of natural accounts. Accounts store financial data for entities and scenarios in an application. Each account has a type, such as Revenue or Expense that defines its accounting behavior. You define attributes for Account dimension members, such as the account type, the number of decimal places to display, and whether the account is a calculated, consolidated, or intercompany partner account. ©Business Intelligence Solution Providers learnhyperion.wordpress.com aloo_a2@yahoo.com 19
- 20. http://learnhyperion.wordpress.com Intercompany Dimension The Intercompany dimension represents all intercompany balances that exist for an account. This is a reserved dimension that is used in combination with the Account dimension and any custom dimension. Financial Management can track and eliminate intercompany transaction details across accounts and entities. You can also run intercompany matching reports to view intercompany transactions. ©Business Intelligence Solution Providers learnhyperion.wordpress.com aloo_a2@yahoo.com 20
- 21. http://learnhyperion.wordpress.com View Dimension The View dimension represents various modes of calendar intelligence; for example, Periodic, Year-to-Date, and Quarter-to-Date frequencies. If you set the view to Periodic, the values for each month are displayed. If you set the view to Year-to-Date or Quarter-to-Date, the cumulative values for the year or quarter are displayed. Custom Dimensions Four custom dimensions are available for analysis of detailed data. You can use custom dimensions to store additional details associated with accounts, such as products, markets, channels, balance sheet movement, or types of elimination. For example, custom dimensions could include Product Line, Region, Channel, or Customers. ©Business Intelligence Solution Providers learnhyperion.wordpress.com aloo_a2@yahoo.com 21
- 22. http://learnhyperion.wordpress.com Dimensions You create metadata for applications by defining dimensions. Dimensions describe your organization’s data. Examples of dimensions are Account, Entity, and Period. The elements that comprise a dimension are called members. For example, GrossMargin and TotalRevenues are members of the Account dimension. ©Business Intelligence Solution Providers learnhyperion.wordpress.com aloo_a2@yahoo.com 22
- 23. http://learnhyperion.wordpress.com Dimension Hierarchies Members of a dimension are arranged in hierarchies. Upper-level members are called parent members, and a member immediately below a parent member is referred to as its child. All members below a parent are referred to as descendants. The bottom-level members of the hierarchy are called base-level members. The illustration in the slide shows a part of the dimension hierarchy of the Account dimension. In this hierarchy, the Total Revenues member is a child of Gross Margin. Sales, Other Revenues, Salaries, Total Revenues, and Total Costs are descendants of Gross Margin. Sales, Other Revenues, and Salaries are base-level members. ©Business Intelligence Solution Providers learnhyperion.wordpress.com aloo_a2@yahoo.com 23
- 24. http://learnhyperion.wordpress.com Dimensions and Data Data is typically entered into base-level members of dimensions and not into parent members. Values for parent-level members are aggregated from the children of the parent-level members. In some cases, data for base-level members is calculated. For example, the Salaries account member might be a base-level member whose value is calculated based on head count and salary rate. In the illustration in the slide, the data values from the base-level members are rolled up to the parent-level members—Total Revenues and Total Costs. Data values from Total Revenues and Total Costs are then rolled up to their parent, Gross Margin. ©Business Intelligence Solution Providers learnhyperion.wordpress.com aloo_a2@yahoo.com 24
- 25. http://learnhyperion.wordpress.com Financial Consolidation Consolidation is the period–end process of combining the financial results of separate subsidiaries with the parent company to form a single, combined statement of financial results. Consolidation is the process of gathering data from descendants and aggregating the data to parent entities. Consolidation applying only to Entity dimension. After loading or entering data into base level entities we run a consolidation for a selected scenario or period to aggregate data throughout the organization. Steps to perform consolidation ©Business Intelligence Solution Providers learnhyperion.wordpress.com aloo_a2@yahoo.com 25
- 26. http://learnhyperion.wordpress.com Before Consolidate After Consolidate When you consolidate an entity, the processes are required for the descendants of the entity run automatically. • Calculation rules are run for all descendants of the entity for the period being consolidate and for all prior periods • If the data for the children & parent entities are in different currencies the data is translated based on the exchange rate. • Intercompany transactions between entities are eliminated at their first common parent. • Data is consolidated from base level entities to parent entities. ©Business Intelligence Solution Providers learnhyperion.wordpress.com aloo_a2@yahoo.com 26
- 27. http://learnhyperion.wordpress.com FINANCIAL CLOSING The financial close process is important to a company as it is the function directly related to producing company financial results for each period end. Restricting access to accounting and reporting applications and establishing clear write-off and reserve policies are examples of financial close process controls. These controls can be preventive or detective in nature. Financial Close Management Streamline the process of Fast Closing • Analysis of process closing (Closing Fast) • Monitoring Process • Calendar of activities • Single Task List • Automatic Workflow • Ensuring Compliance • Email and calendaring ©Business Intelligence Solution Providers learnhyperion.wordpress.com aloo_a2@yahoo.com 27
- 28. http://learnhyperion.wordpress.com (E.g. Outlook) FCM: different visions of the process Process Monitoring •Illustrate the current status of all process in a simple and intuitive Dashboards and reporting the ad-hoc offer a complete and immediate understanding in real time closing process • Automatically update the states tasks assigned to the process • Highlights that the tasks are risk or delay • Encourage users to improve closing process Active Financial Close Calendar • Detail all the tasks necessary the closure process accountant • Provides multiple views of workflow process Calendar Task list Gantt • Customizable for each user Task Management • Assignment of tasks in most types of function of different processes Milestone tasks • Access and use for each user • Integrates with tasklist systems EPM and EBS (eg AR sub ledger close to GL) • Enables automation of processes complex • Supports management hierarchies processes, dependencies and associations • Activities can be incorporated Systems email / calendar (MS Outlook, others) ©Business Intelligence Solution Providers learnhyperion.wordpress.com aloo_a2@yahoo.com 28